Language Server Protocol (LSP)
LSP is a standardization between “development tools” (vscode, emacs, intellij, vim, …) and “language servers” (clangd, typescript-lang-server…)
Reading
What is the LSP?
- the idea behind a language server is to provide the language-specific smarts inside a server that can communicate with development toolings that enables inter-process communication.
- the idea behind the language server protocol is to standardize the protocol for how tools and servers communicate, so a single language server can be re-used in multiple development tools, and tools can support languages with minimal effort.
How the LSP works
-
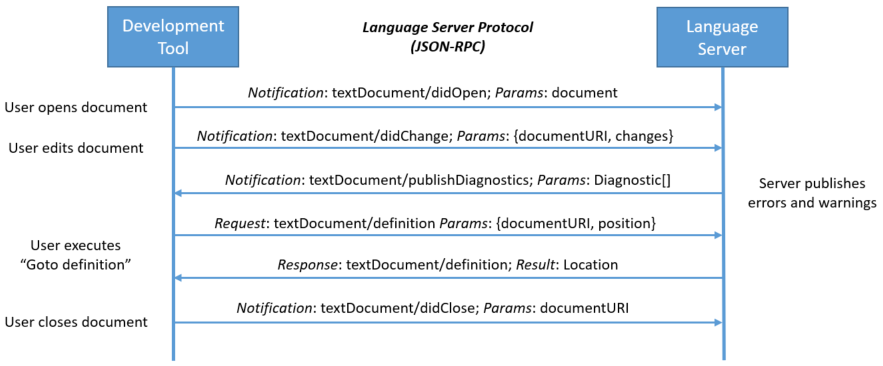
the language protocol is communicated over JSON-RPC
-
Interactions between dev tool and lang server during routine editing session
-
the user opens a file in the tool
- kept in-memory by tool and must be synced between tool and lang server
- the user makes edits and dev tool notifies the server
-
the user executes “Go to Definition” on a symbol of an open document
- The dev tool sends a request with two params: (1) the document URI and (2) the text position from wherre the go to request was iniated to the server.
- The language server responds with the document URI and the position of your symbol’s definition inside the document
- The user closes the document (file), no longer in-memory, and file system is up to date.
-
the user opens a file in the tool
-
Not every language server has autocomplete, or documentation, etc. so LSP therefore provides ‘capabilities’.
- capabilties group sets of language features that annouces the presence of a language server.
-
Interactions between dev tool and lang server during routine editing session
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration refers to the practice of automatically and frequently integrating code changes into a shared source code repository.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment is the process that follows a factory to adapt their changes by creating a special build process for their different product. This build process consists these steps:
- Fetching dependencies from repo
- Building codes
- Running automated tests on this build
- Running code analytics
- Notification to Developers about feedback (error, success, warnings, etc.)
- Packaging the build for Continuous Delivery